The Use of Big Data in
Supply Chain Optimization
The global supply chain manages the sourcing of a high volume of products, in transit at different velocities, and satisfying a variety of customers. This intricate network generates numerous data points; if analyzed appropriately it yields valuable information. Big data analytics revamp the traditional supply chain management practices by utilizing the vast volume, variety, and velocity of information to optimize processes and improve decision making resulting in a resilient digital supply chain.
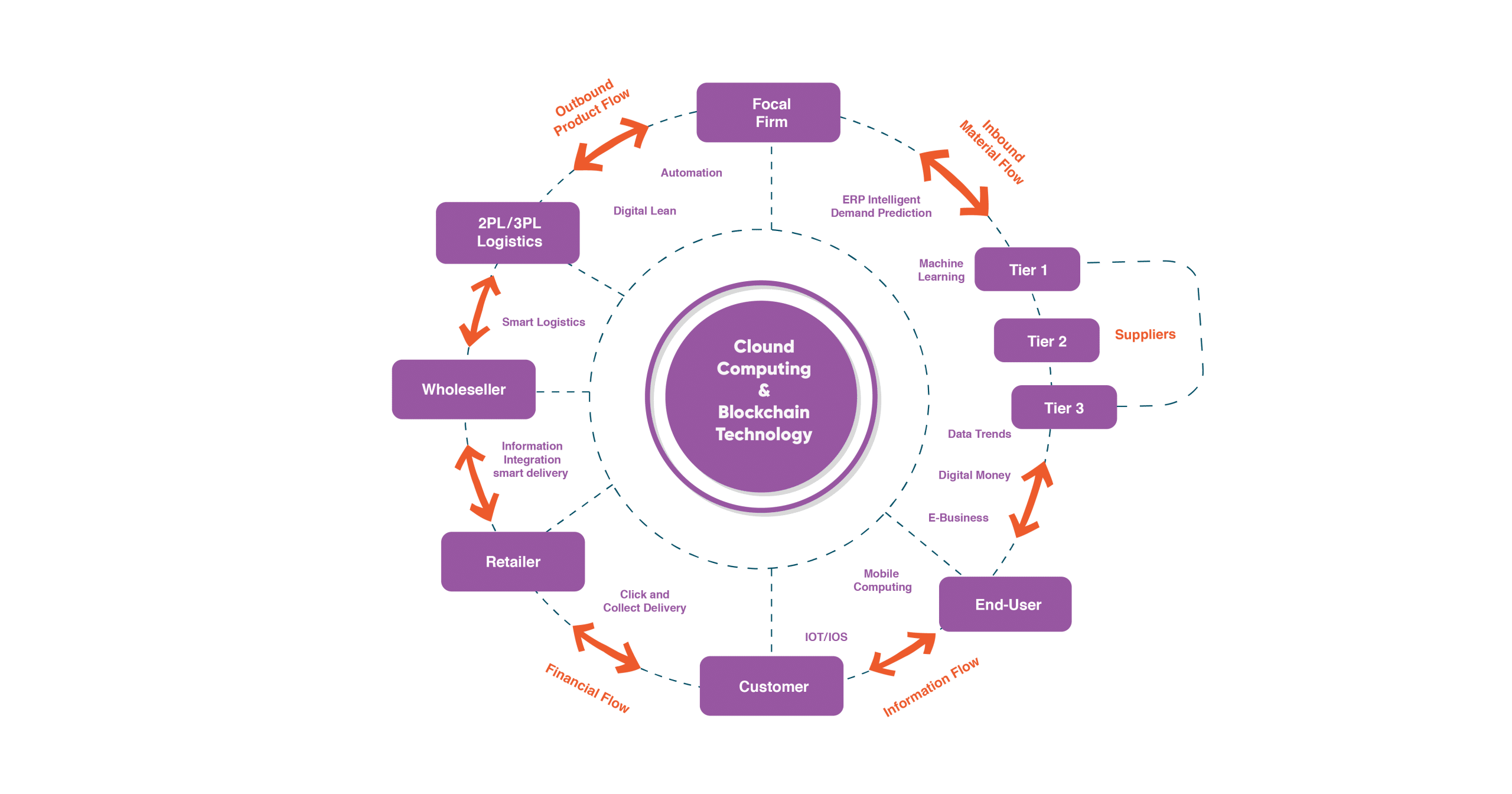
A digital supply chain (DSC) incorporates physical products, software, knowledge, infrastructure, and services using techniques like advanced data analytics (AA), big data processing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI). In a digital supply chain network structure, all parties; tier 1,2,3 suppliers, second & third-party logistics, focal firm, fourth- & fifth-part logistics, wholesaler, distributor, retailer, and end consumer; are connected via intelligent technological systems. Data from different supply chain flows; inbound material flow, outbound product flow, financial flow, information flow, and service flow is analyzed and transmitted at vital points in time. Macro interconnectivity is established among these components using Industry 4.0 technology enablers which facilitates the management processes in the DSCs. Oettmeier and Hofmann have identified the core management processes of the supply chain in their research titled “Impact of additive manufacturing technology adoption on supply chain management processes and components”. Incorporating big data within these management processes produces valuable outcomes that facilitate informed decision-making and enhance the optimization of the supply chain network.
Implementing Big Data Techniques across the Core Management Processes in Supply Chain
The successful implementation of advanced big data techniques within the core management processes of the supply chain involves a strategic and data-driven approach. The right analysis of data harmonizes supply chain flows and management procedures, which attains competitive advantage across both inter-company and intra-company contexts.
Supplier Relationship Management
Blockchain technology efficiently oversees the dynamics between buyers and suppliers. To begin with, information is sourced from communication channels, financial records, delivery schedules, quality assessments, and response durations. This data is then centralized and meticulously scrutinized, with distinct Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) being established. This in-depth analysis gives rise to trends that show the performance of each supplier. Through predictive analysis methods, patterns within these trends are deciphered, revealing potential risks tied to each supplier that can be proactively managed.
The integration of digital applications, the Internet of Things (IoT), and proximity technologies aids in amassing data relevant to forecasting and order processing. This data-driven approach facilitates the effective segmentation of suppliers based on their characteristics and capabilities. Additionally, for trusted suppliers, the option of harnessing Smart Contracts is extended, yielding substantial reductions in both processing time and associated expenses. These Smart Contracts are pre-programmed agreements embedded within the system, ingeniously designed to renew automatically once predetermined conditions are met.
Customer Relationship Management
Information gathered from both structured and unstructured sources plays a pivotal role in customer profiling. Employing big data analytics, trends emerge from a multitude of sources, including demography, facial recognition, online interactions, geolocation, E-commerce history, and social networks. This intricate analysis yields invaluable insights, enabling product personalization to suit specific customer preferences.
A striking example of this is Amazon’s patent for predictive shipping, a novel application of data analytics. This revolutionary approach anticipates the behavior of potential customers and initiates the shipment process even before an order is placed, significantly slashing delivery times. The timely push notification and the careful observation of clicks per page ensure that the right product is presented to the customer at the most opportune moment. Through these techniques, the transformation of a potential customer into an actual one is facilitated. Such strategic product placement has proven immensely advantageous for corporations. Netflix, for instance, has adeptly adopted this strategy, resulting in increased revenues. By showcasing content that aligns with users’ preferences, based on their past viewing habits, Netflix maximizes viewer engagement.
In essence, the fusion of diverse data sources and advanced analytics is redefining customer engagement. By accurately predicting and catering to customer needs, companies are poised to foster deeper connections, optimize sales, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
Demand Management
Demand forecasting is a complex endeavor influenced by many factors; quality, competitors, substitutes, fashion trends, buying behavior, weather, events, religion, demographics, marketing efforts, product availability, and consumer preference. Data mining techniques possess the capacity to concurrently visualize and analyze all these factors, comparing & contrasting them against each other to forecast trends that surpass the processing capabilities of humans. Unstructured data from social media, surveys, and social networks is analyzed using the NoSQL database provides visualization and detailed reports of customers. This data exploration, when accompanied by advanced analytics generates descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive models that help in demand management. A leading fast fashion supplier has predicted accurate demands using analysis of social media sentiments and fast-track their delivery.
Order Fulfillment
The utilization of technology enables the smoothing of customer journeys and the innovation of the order fulfillment process. Big data plays a significant role in optimizing inventory by Just in Time (JIT) deliveries through its accurate demand predictions. Interlinking point-of-sale data with supplier performance data results in accurate inventory level information, effectively reducing both warehousing efforts and holding costs. Route optimization, facilitated by data analytics, emerges as another advantageous outcome that efficiently cuts costs and decreases delivery durations. Data insights further contribute to the refinement of order prioritization, relying on the significance of customers determined through past profiling. Real-time tracking facilitated by RFID devices and proximity sensors furnishes precise information at any point along the supply chain. The GS1 coding system emerges as a highly beneficial tool in this context. Additionally, effective returns management is also positively influenced by data analysis. A comprehensive analysis of past returns aids in reducing risks associated with future purchases, and it also provides quality and reliability data for supplier performance assessment. The simulation modeling significantly heightens operational efficiency, achieved through the continuous improvement mechanisms of automation, real-time visibility, and transparency via real-time monitoring. Furthermore, services are optimized through predictive analysis.
Datafication has impacted our lives and businesses alike. Industries need to revamp their supply chains to account for fluctuating business conditions, changing customer demands, and holistic market trends. A fully integrated DSC is an asset for the focal company. However, this data-driven approach can only be impactful if accompanied by the organization’s fit and favorable cultural dynamics.